Periodontal diseases are infections of the gums, which gradually lead to the destruction of the support of your natural teeth. These diseases affect more than 80% of Americans by age 45.
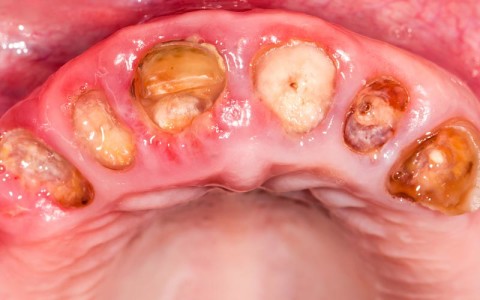
Dental plaque is the primary cause of gum disease. Bacteria found in plaque produce enzymes and toxins which injure the gums. Injured gums turn red, swell and bleed easily. If this injury is prolonged, the gums separate from the teeth, causing pockets (spaces) to form.
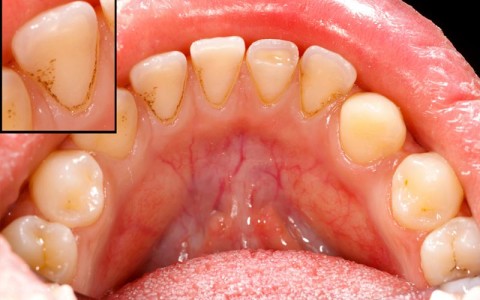
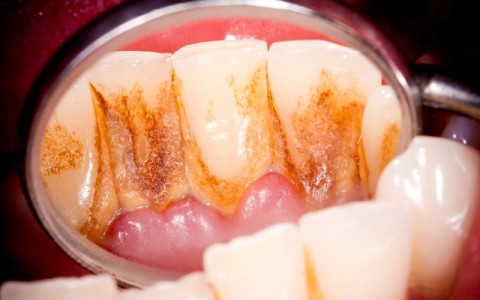
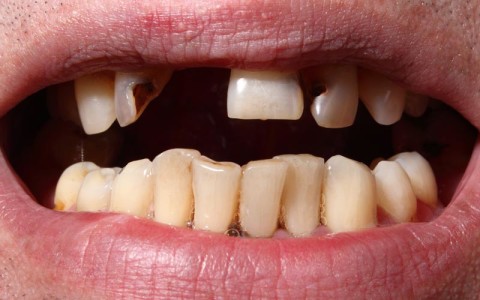
Plaque can also harden into a rough, porous substance known as calculus (tartar). This can occur both above and below the gum line. As periodontal diseases progress, the supporting gum tissue and bone that holds teeth in place deteriorate.
Diseases that interfere with the body’s immune system may worsen the condition of the gums. If you suffer from an uncontrolled systemic disease such as osteoporosis, diabetes, immune system deficiency or others, seeing a periodontist can help you avoid gum disease.